What Has the Largest Effect on Atmospheric Wind Patterns
The shift in winds results from unequal heating of the land and water. This the pressure gradient and the Coriolis effect interact by interact by.

Global Atmospheric Circulations Physical Geography
Research publishing in the journal Joule on October 4 reports the most accurate modelling yet of how increasing wind power would affect climate finding that large-scale wind power generation would.

. Convection currents cause winds to blow from the sea toward the land. The _____ contains 90 of all. The properties of the atmosphere affect all the weather that is created within it.
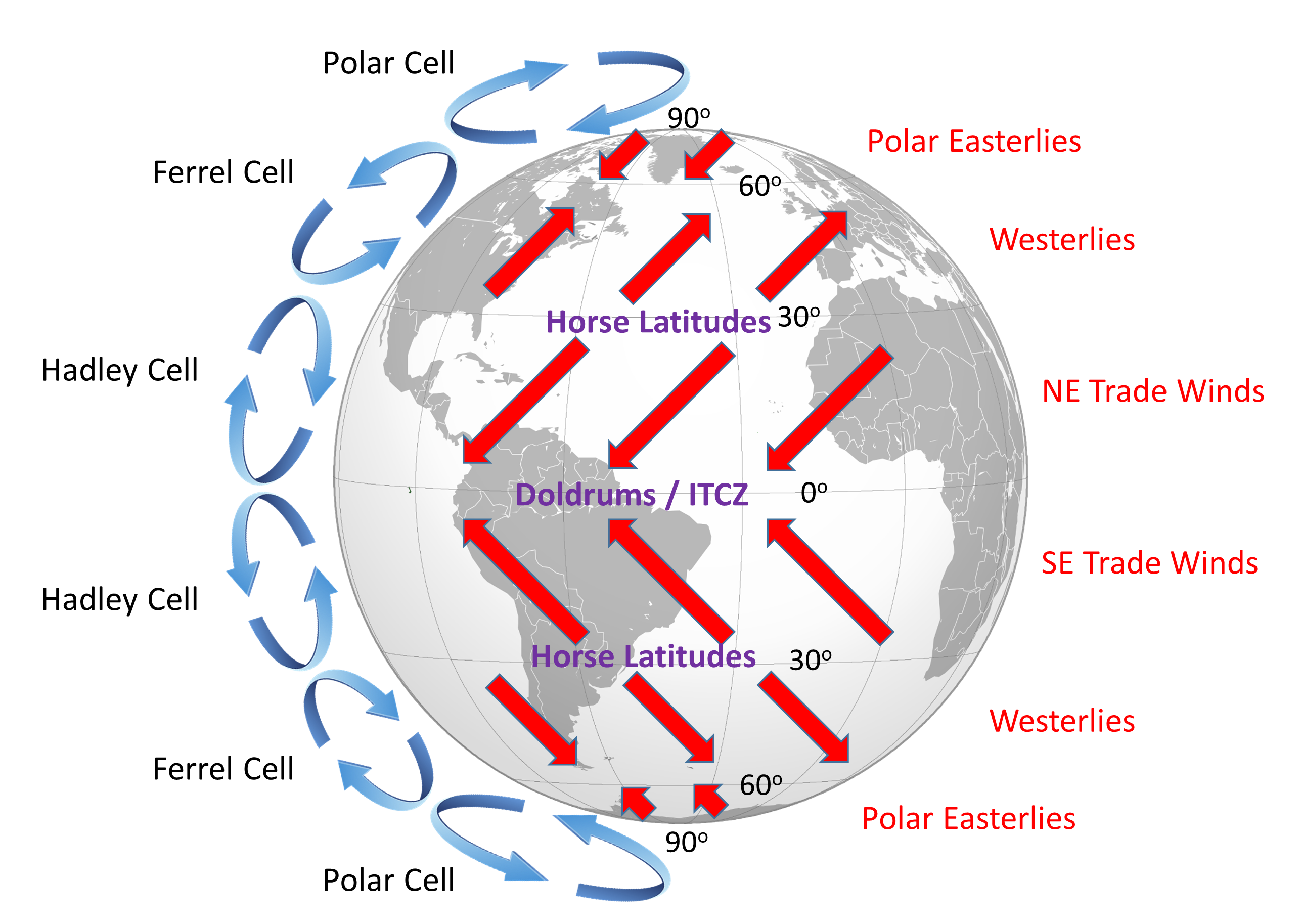
The pattern reverses at night. At 60 N part of the rising air mass goes north and part goes south. Note that the US.
Formation of clear air turbulence CAT responsible for air pockets. The wind and how it behaves has the biggest impact on your flight. The stronger the vertical wind shear.
Air masses cool and sink at 30 N at the northern edge of the trade wind cell. It would be nice if pressure. Global Wind Patterns Visualization NASA Simulation compiled from a series of animations showing global wind patterns at two different levels in the atmosphere.
The most obvious effect is that of absorption most radiation incident on the Earths upper atmosphere does not reach the ground. Over the rough surface where frictional forces are much larger winds cross the isobars at an angle of 45 degrees. The strongest band of winds aloft is called the jet stream.
The movement of air masses brings us our daily weather and long-term patterns in circulation determine regional climate and. Which of the following has the largest effect on atmospheric wind patterns. Coriolis effect As they travel across the Earth air masses and global winds do not move in straight lines.
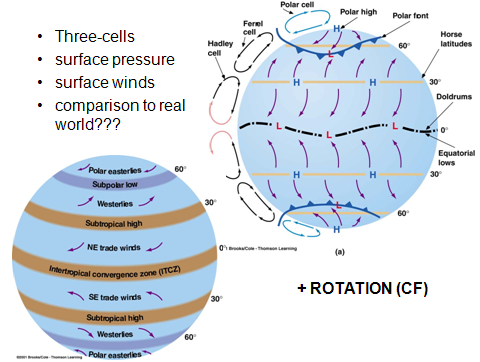
Atmospheric circulation transports heat over the surface of the Earth that affects the water cycle including the formation of clouds and precipitation events. The two main factors affecting wind patterns are 1 the heat distribution between the earths equator and poles and 2 the constant rotation of the planet. The sinking air mass also splits at 30 N with part going north and part returning south.
High in the atmosphere narrow bands of strong wind such as the jet streams steer weather systems and transfer heat and moisture around the globe. Thus the Ferrel cell is like an atmospheric gear driven by the Hadley and polar circulation cells. Atmospheric Weather Wind Patterns - Chapter Summary.
This includes the entire visible region 390 nm 780 nm plus the near ultraviolet near infrared and some. Is created during the day when radiation warms the air over the land more than the air over the water causing winds to blow in from the sea. Over the sea surface the friction is minimal.
Frictional Force and Wind Movement. It is greatest at the surface and its influence generally extends up to an elevation of 1 3 km. The winds aloft are strongest near the largest horizontal temperature gradient.
In addition the greater heatingcooling contrast in winter yields stronger pressure differences during this season. Gravitational pull of sun and moon. However the environment far above us impacts their movement.
Each of these wind belts represents a cell that circulates air through the atmosphere from the surface to high altitudes and back again. The stronger the horizontal temperature gradient the stronger the thermal wind. The strength of the animation is that temperature values can be compared throughout the day and then linked to wind patterns.
Wind shear occurs at all altitudes and it can be horizontal or vertical At high altitudes shear is encountered at the jet stream with the wind increasing from less than 50 mph to 150 mph over a few miles. The illustration below portrays the global wind belts three in each hemisphere. From how bumpy it is to how likely it is to be delayed.
The irregularities of the earths surface offer resistance to the wind movement in the form of friction. During the day land heats more rapidly than the water air rises and a cool breeze blows in from the water. It affects the speed of the wind.
Trade Winds NOAA Explains the formation movement and coupling of Earths trade winds. Transient eddies such as extratropical. Here the speed of wind may also be reduced by as much as 5 per cent.
The atmosphere is effectively opaque to all but some radio wavebands and light in the optical window. The sun is Earths primary energy source. So many factors have an impact on weather.
The winds aloft can change direction if the horizontal temperature gradient changes direction. However energy from sunlight is not evenly distributed over the earths surface. Convection currents cause winds to blow from the land toward the sea.
These fun informative video lessons explain how air. Lies primarily in the Westerly Wind Belt with prevailing winds from the west. Depth of the sea.
During a meridional flow areas of low pressure can become stuck over the UK leading to prolonged periods of rain and strong winds. Global Circulations NOAA Looks at global atmospheric circulation patterns and how they influence climate and weather. The apparent deflection of anything moving horizontally to the right of its direction of travel in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere.
Changes in stationary eddy circulationswind patterns due to the presence of continents and warm ocean regionsdominate regional precipitation changes. As noted above winds in the lowest layers of atmosphere are greatly influenced by. Excess heating in tropical latitudes in contrast to polar areas produces higher pressure at upper levels in the tropics as thunderstorms transfer air to higher levels.
Next week Ill be explaining the other main parts of the weather that can affect your flight thunderstorms and fog.

Atmospheric Circulation Meteorology Britannica

A Global Look At Moving Air Atmospheric Circulation Center For Science Education
8 2 Winds And The Coriolis Effect Introduction To Oceanography
No comments for "What Has the Largest Effect on Atmospheric Wind Patterns"
Post a Comment